B2B Mastery: 7 Ultimate Strategies for Explosive Growth
If you’ve ever wondered why some companies thrive while others struggle, the secret often lies in their B2B strategy. Welcome to the ultimate guide on B2B mastery—where we break down what it really takes to dominate in the business-to-business world.
What Exactly Is B2B? A Deep Dive into Business-to-Business Models

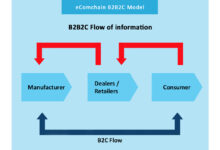
The term b2b might seem simple at first glance, but its implications are vast and transformative. At its core, B2B refers to transactions between businesses, such as a manufacturer selling to a wholesaler or a software company licensing tools to another enterprise. Unlike B2C (business-to-consumer), B2B relationships are built on logic, long-term value, and complex decision-making processes.
Defining B2B in Modern Commerce
B2B isn’t just about selling products; it’s about solving problems at scale. According to Investopedia, B2B involves commercial transactions between organizations, often involving high-volume orders and contractual agreements. These transactions form the backbone of global supply chains, from raw materials to digital services.
- B2B transactions typically have higher order values than B2C.
- Decision-making involves multiple stakeholders (e.g., procurement, finance, IT).
- Sales cycles are longer but result in more stable revenue streams.
How B2B Differs from B2C
While B2C focuses on emotional triggers and instant gratification, B2B thrives on ROI, efficiency, and strategic alignment. A consumer might buy a coffee maker on impulse, but a company purchasing enterprise software will evaluate vendors for months. As Forbes highlights, B2B buyers expect detailed data, case studies, and proof of performance before committing.
“In B2B, you’re not just selling a product—you’re selling peace of mind, scalability, and competitive advantage.”
The Evolution of B2B: From Fax Machines to Digital Marketplaces
The landscape of b2b has undergone a radical transformation over the past few decades. What once relied on phone calls, trade shows, and paper catalogs now thrives on AI-driven platforms, e-procurement systems, and data analytics.
Historical Milestones in B2B Commerce
In the 1980s, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) revolutionized how businesses exchanged invoices and purchase orders. Fast forward to the 1990s, and the rise of the internet introduced early B2B marketplaces like Alibaba (founded in 1999). These platforms allowed small suppliers to connect with global buyers, democratizing access to international markets.
- 1980s: EDI enables automated order processing.
- 1990s: The internet spawns online B2B directories and portals.
- 2000s: CRM systems like Salesforce transform B2B sales workflows.
The Digital Revolution and E-Commerce Integration
Today, B2B e-commerce is projected to reach $20.9 trillion by 2027, according to McKinsey. Platforms like Amazon Business and ThomasNet have made it easier than ever for companies to discover, compare, and purchase products online—mirroring the B2C experience.
The integration of AI chatbots, personalized dashboards, and automated reordering systems has elevated customer expectations. Buyers now demand seamless, self-service experiences similar to what they enjoy as consumers.
Key Components of a Successful B2B Strategy
Winning in the b2b space requires more than just a great product. It demands a holistic strategy that aligns sales, marketing, customer success, and technology.
Target Market Identification and Segmentation
Not all businesses are your ideal customers. Effective B2B strategies begin with precise market segmentation. Are you targeting SMBs, mid-market firms, or enterprise clients? Each segment has distinct needs, budgets, and decision-making structures.
- Use firmographic data (industry, company size, revenue) to segment prospects.
- Leverage technographic insights to understand existing tech stacks.
- Apply behavioral data to identify buying patterns and engagement levels.
Value Proposition Development
Your value proposition must answer one critical question: “Why should a business choose you?” It’s not enough to say you’re “reliable” or “innovative.” You need quantifiable outcomes—like “Reduce operational costs by 30% within six months” or “Increase team productivity by 45% with AI-powered automation.”
“A strong B2B value proposition doesn’t sell features—it sells transformation.”
Sales Funnel Optimization
The B2B sales funnel is inherently longer and more complex than its B2C counterpart. It typically includes stages like awareness, consideration, evaluation, purchase, and retention. Optimizing each stage requires tailored content, nurturing campaigns, and CRM integration.
- Awareness: Publish whitepapers, webinars, and SEO-optimized blog posts.
- Consideration: Offer product demos, free trials, and comparison guides.
- Decision: Provide ROI calculators, case studies, and contract negotiation support.
B2B Marketing: Tactics That Drive Real Results
Marketing in the b2b world is less about flashy ads and more about building trust through consistent, value-driven communication.
Content Marketing and Thought Leadership
One of the most effective B2B marketing tools is content that educates and inspires. Companies like HubSpot and Salesforce have built empires by offering free resources—blogs, templates, certifications—that position them as industry leaders.
- Create in-depth guides on industry challenges (e.g., “How to Optimize Supply Chain Resilience”).
- Host expert roundtables and publish research reports.
- Repurpose content across formats: turn a webinar into a blog series, infographic, and podcast.
Email Nurturing and Lead Scoring
Not all leads are ready to buy. Email nurturing campaigns help move prospects through the funnel by delivering relevant content based on their behavior. Lead scoring assigns points to actions (e.g., downloading a whitepaper, attending a demo), helping sales teams prioritize high-intent prospects.
According to MarketingProfs, nurtured leads make 47% larger purchases than non-nurtured ones.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
ABM flips traditional marketing on its head by focusing on specific high-value accounts rather than broad audiences. Instead of casting a wide net, ABM targets decision-makers within a single organization with personalized campaigns.
- Identify target accounts using intent data and firmographics.
- Create custom landing pages, emails, and ads for each account.
- Align sales and marketing teams to engage key stakeholders simultaneously.
The Role of Technology in Modern B2B Operations
Technology is no longer a support function in b2b—it’s the engine driving growth, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
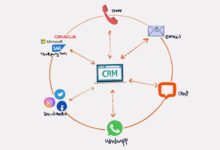
CRM Systems and Automation Tools
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho are essential for managing interactions, tracking deals, and analyzing performance. When integrated with marketing automation tools (e.g., Marketo, Pardot), they enable end-to-end visibility across the customer journey.
- Automate follow-ups and task reminders to reduce manual workload.
- Track customer interactions across email, phone, and social media.
- Generate real-time reports on pipeline health and conversion rates.
AI and Predictive Analytics in B2B
Artificial Intelligence is transforming how B2B companies forecast demand, personalize outreach, and prevent churn. Predictive analytics can identify which leads are most likely to convert or which customers are at risk of leaving.
For example, Gong.io uses AI to analyze sales calls and provide coaching insights, while Clari leverages machine learning to improve forecast accuracy. As Gartner notes, by 2025, 75% of B2B sales organizations will use AI for sales forecasting and coaching.
E-Commerce Platforms and Self-Service Portals
Modern B2B buyers expect the same convenience they get from B2C sites. Self-service portals allow customers to place orders, track shipments, download invoices, and access support without human intervention.
- Implement B2B-specific e-commerce platforms like Magento B2B or Shopify Plus.
- Offer tiered pricing, volume discounts, and contract-based purchasing.
- Integrate with ERP systems for real-time inventory and billing updates.
B2B Sales: Mastering the Art of Complex Deal-Making
Selling in the b2b space is a high-stakes game that requires patience, precision, and deep industry knowledge.
Consultative Selling Techniques
Gone are the days of pushy sales tactics. Today’s B2B buyers respond to consultative selling—where reps act as advisors, diagnosing pain points and co-creating solutions.
- Ask open-ended questions to uncover hidden challenges.
- Listen more than you talk during discovery calls.
- Present tailored recommendations backed by data and case studies.
Building Long-Term Client Relationships
In B2B, the sale is just the beginning. Retention is where real profitability lies. A 5% increase in customer retention can boost profits by 25% to 95%, according to Harvard Business Review.
“The goal isn’t to close a deal—it’s to start a partnership.”
Strategies for building lasting relationships include regular check-ins, proactive support, and continuous value delivery through training, updates, and strategic reviews.
Negotiation and Contract Management
B2B deals often involve multi-year contracts, service-level agreements (SLAs), and complex pricing models. Effective negotiation balances firmness on value with flexibility on terms.
- Prepare thoroughly: know your client’s budget, goals, and constraints.
- Use anchoring techniques to set favorable price expectations.
- Leverage legal and finance teams to draft clear, enforceable contracts.
Measuring B2B Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. In b2b, tracking the right KPIs is crucial for assessing performance and guiding strategy.
Revenue and Growth Metrics
While total revenue is important, deeper metrics provide more insight:
- Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR): Predictable revenue from subscriptions or contracts.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Total sales and marketing spend divided by new customers acquired.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Total revenue expected from a customer over their relationship with your company.
A healthy B2B business typically has a CLTV:CAC ratio of 3:1 or higher.
Customer Satisfaction and Retention
Happy customers stay longer and refer others. Key indicators include:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures willingness to recommend your company.
- Churn Rate: Percentage of customers who stop doing business with you.
- Customer Effort Score (CES): How easy it is for customers to get issues resolved.
Sales and Marketing Efficiency
These KPIs help assess the effectiveness of your go-to-market engine:
- Lead Conversion Rate: Percentage of leads that become customers.
- Sales Cycle Length: Average time from first contact to closed deal.
- Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) to Sales Qualified Lead (SQL) Ratio: Indicates alignment between marketing and sales.
Future Trends Shaping the B2B Landscape
The b2b world is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovation, changing buyer expectations, and global economic shifts.
Rise of AI-Powered Personalization
AI is enabling hyper-personalized experiences at scale. From dynamic pricing to customized content delivery, businesses can now tailor every interaction to the individual buyer’s role, industry, and past behavior.
For instance, AI-driven platforms like 6sense use intent data to predict which accounts are actively researching solutions, allowing sales teams to engage at the perfect moment.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in B2B
More companies are prioritizing sustainability in their procurement decisions. A 2023 IBM study found that 68% of B2B buyers consider a supplier’s environmental impact when making purchasing decisions.
- Highlight your carbon footprint reduction initiatives.
- Obtain sustainability certifications (e.g., ISO 14001).
- Partner with eco-conscious logistics providers.
Globalization and Cross-Border B2B Commerce
Digital platforms have erased geographical barriers. A manufacturer in Germany can now easily sell to a distributor in Indonesia through B2B marketplaces.
However, cross-border trade introduces complexities like currency fluctuations, regulatory compliance, and cultural differences. Companies must invest in localization, multilingual support, and international payment gateways to succeed globally.
What is B2B and how does it differ from B2C?
B2B, or business-to-business, refers to transactions between two companies, such as a software firm selling to a corporation. Unlike B2C (business-to-consumer), B2B sales involve longer decision cycles, multiple stakeholders, and a focus on ROI and operational efficiency rather than emotional appeal.
What are the most effective B2B marketing strategies?
The most effective B2B marketing strategies include content marketing, account-based marketing (ABM), email nurturing, and thought leadership. Success hinges on delivering value, building trust, and aligning sales and marketing efforts around high-intent prospects.
How important is technology in B2B operations?
Technology is critical in modern B2B operations. CRM systems, AI-driven analytics, e-commerce platforms, and automation tools streamline sales, enhance customer experience, and provide data-driven insights for strategic decision-making.
What are common KPIs used to measure B2B success?
Common B2B KPIs include Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR), Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV), Net Promoter Score (NPS), churn rate, and sales cycle length. These metrics help assess financial health, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
What future trends will shape B2B commerce?
Future trends include AI-powered personalization, increased focus on sustainability, globalization of B2B markets, and the rise of self-service digital platforms. Companies that adapt to these shifts will gain a competitive edge in the evolving B2B landscape.
Mastering B2B is not about quick wins—it’s about building sustainable, value-driven relationships that stand the test of time. From understanding the fundamentals to leveraging cutting-edge technology and anticipating future trends, the path to B2B excellence requires strategy, discipline, and continuous innovation. Whether you’re a startup entering the market or an established player scaling globally, the principles outlined in this guide provide a roadmap for explosive growth and long-term success in the dynamic world of business-to-business commerce.
Further Reading: