B2B Business Secrets: 7 Proven Strategies for Explosive Growth
Ever wonder why some companies thrive while others barely survive? The secret often lies in mastering the art of B2B business—where relationships, strategy, and precision drive long-term success.
What Exactly Is a B2B Business?

The term B2B business, or business-to-business, refers to transactions between companies rather than between a company and individual consumers (B2C). This model powers global supply chains, tech ecosystems, and industrial markets. Unlike B2C, where emotions often drive purchases, B2B decisions are typically rational, data-backed, and involve multiple stakeholders.
Defining B2B vs. B2C
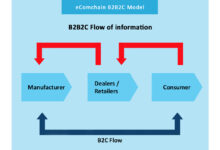
While both models involve selling products or services, the core difference lies in the buyer. In a B2B business, the customer is another organization—like a manufacturer buying raw materials or a SaaS company selling software to enterprises. In contrast, B2C targets individual end-users.
- B2B sales cycles are longer and more complex.
- B2B purchases involve higher order values and contracts.
- Decision-making in B2B often requires approval from multiple departments.
“B2B is not just about selling to businesses—it’s about solving their business problems.” — Marc Benioff, CEO of Salesforce
Common Examples of B2B Business Models
From cloud computing to industrial equipment, B2B spans countless industries. Some prominent examples include:
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Companies like Salesforce and Microsoft sell enterprise software solutions.
- Manufacturing & Supply Chain: Firms like 3M supply components to other manufacturers.
- Wholesale Distribution: Distributors sell bulk goods to retailers or other businesses.
These models thrive on long-term contracts, recurring revenue, and deep integration with client operations.
Why B2B Business Is More Profitable Than You Think
Many entrepreneurs overlook B2B, assuming consumer markets are more lucrative. But the reality? B2B often delivers higher margins, stronger customer loyalty, and more predictable revenue streams. According to Statista, the global B2B e-commerce market is projected to reach $20.9 trillion by 2027—nearly double the size of B2C e-commerce.
Higher Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
In a typical B2B business, the lifetime value of a single client can be exponentially higher than in B2C. A SaaS platform charging $10,000/month per enterprise client can generate $120,000 annually from just one account. Multiply that by dozens of clients, and the scalability becomes clear.
- B2B clients often sign multi-year contracts.
- Upselling and cross-selling are easier due to deep integration.
- Support and service add-ons increase revenue per client.
Lower Customer Acquisition Costs Over Time
While initial B2B sales cycles can be long and resource-intensive, the long-term cost of acquisition (CAC) decreases as relationships mature. Once trust is established, renewals and expansions happen with minimal marketing effort.
- Referrals from existing clients reduce ad spend.
- Content marketing and thought leadership build organic authority.
- Account-based marketing (ABM) increases conversion efficiency.
“The best salespeople in B2B don’t sell products—they sell outcomes.” — Jill Konrath, Author of ‘Selling to Big Companies’
The 7 Key Pillars of a Successful B2B Business
Building a thriving B2B business isn’t about luck—it’s about strategy. Here are seven foundational pillars that separate average companies from industry leaders.
1. Deep Market Understanding
Before you sell anything, you must understand your target market’s pain points, workflows, and decision-making hierarchies. This requires more than surface-level research—it demands empathy.
- Conduct interviews with potential clients.
- Analyze industry reports from sources like Gartner or McKinsey.
- Map out buyer personas for each stakeholder (e.g., CFO, CTO, procurement manager).
Without this insight, your messaging will miss the mark.
2. Value-Driven Messaging
In a B2B business, customers don’t buy features—they buy results. Your marketing and sales materials should focus on ROI, efficiency gains, risk reduction, or compliance improvements.
- Replace “Our software has AI analytics” with “Reduce operational costs by 30% using AI-driven insights.”
- Use case studies to demonstrate real-world impact.
- Highlight time-to-value and implementation speed.
Clear, outcome-focused messaging cuts through the noise.
3. Scalable Sales Process
A repeatable, scalable sales process is the engine of any high-growth B2B business. This includes lead qualification, demo delivery, negotiation, and onboarding.
- Implement a CRM like HubSpot or Zoho to track every interaction.
- Develop sales playbooks for different client segments.
- Train reps to handle objections with data, not just persuasion.
“A great B2B sales process turns complexity into clarity.” — Aaron Ross, Author of ‘Predictable Revenue’
How Digital Transformation Is Reshaping B2B Business
The digital age has revolutionized how B2B companies operate, sell, and retain customers. From AI-powered analytics to automated workflows, technology is no longer optional—it’s the backbone of competitive advantage.
E-Commerce Platforms for B2B
Gone are the days when B2B meant phone calls and PDF catalogs. Today, companies like Grainger and Faire offer seamless online ordering, real-time inventory tracking, and self-service portals.
- Custom pricing based on client tier or volume.
- Integrated procurement systems with ERP software.
- Mobile-friendly interfaces for on-the-go buyers.
These platforms reduce friction and accelerate purchase decisions.
AI and Automation in B2B Operations
Artificial intelligence is transforming everything from lead scoring to customer support. Chatbots handle initial inquiries, predictive analytics forecast demand, and machine learning optimizes pricing strategies.
- AI-driven CRM tools prioritize high-intent leads.
- Automated onboarding reduces time-to-value.
- NLP (Natural Language Processing) analyzes customer feedback at scale.
Companies leveraging AI report up to 30% higher sales efficiency, according to a IBM study.
“AI won’t replace B2B salespeople—but salespeople who use AI will replace those who don’t.” — James Oldroyd, CEO of Zoho Europe
B2B Business Models: Which One Fits Your Company?
Not all B2B businesses operate the same way. Choosing the right model depends on your product, market, and growth goals. Let’s explore the most common types.
1. Product-Based B2B
This model involves selling physical goods to other businesses. Examples include industrial machinery, raw materials, or office supplies.
- Revenue comes from one-time or bulk sales.
- Logistics and supply chain management are critical.
- Customer relationships focus on reliability and delivery speed.
Success hinges on operational excellence and cost efficiency.
2. Service-Based B2B
These companies sell expertise—like consulting, marketing agencies, or IT support.
- Revenue is often project-based or retainer-driven.
- Scalability depends on team capacity and delivery systems.
- Reputation and case studies are key differentiators.
Building a strong brand and client portfolio is essential.
3. Subscription-Based B2B (SaaS)
One of the fastest-growing models, SaaS companies charge recurring fees for software access.
- Predictable revenue through monthly or annual subscriptions.
- High margins after initial development costs.
- Customer success teams ensure retention and expansion.
Platforms like Shopify and Adobe dominate this space by offering scalable, cloud-based solutions.
“The subscription model turns customers into partners.” — Tien Tzuo, CEO of Zuora
Mastering B2B Marketing: Strategies That Actually Work
Marketing in a B2B business isn’t about flashy ads—it’s about building trust, authority, and relevance over time. Here are proven strategies that deliver results.
Content Marketing & Thought Leadership
Decision-makers in B2B environments seek credible information before engaging with vendors. High-quality content positions your brand as a trusted advisor.
- Publish whitepapers, research reports, and industry guides.
- Host webinars featuring subject matter experts.
- Write LinkedIn articles that address common pain points.
According to Content Marketing Institute, 91% of B2B marketers use content marketing to reach customers.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
ABM flips traditional marketing on its head. Instead of casting a wide net, you target specific high-value accounts with personalized campaigns.
- Identify top 50 target companies.
- Create custom content and ads for each.
- Engage multiple stakeholders within the same organization.
ABM can increase conversion rates by up to 50%, per ABM Institute.
“ABM is not a tactic—it’s a philosophy of alignment between sales and marketing.” — Sangram Vajre, Co-Founder of Terminus
The Future of B2B Business: Trends to Watch in 2025 and Beyond
The B2B landscape is evolving at breakneck speed. To stay ahead, companies must anticipate shifts in buyer behavior, technology, and global economics.
Rise of the Digital-First Buyer
Today’s B2B buyers are digital natives. They research independently, compare vendors online, and expect seamless digital experiences.
- 89% of B2B buyers start their journey with a search engine (Google).
- Interactive product demos and virtual sales reps are gaining traction.
- Self-service portals reduce dependency on sales teams.
Companies that optimize for digital discovery will win.
Sustainability as a Competitive Advantage
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are no longer optional. B2B buyers increasingly favor suppliers with sustainable practices.
- Carbon-neutral shipping options.
- Transparent supply chain reporting.
- Recyclable packaging and energy-efficient operations.
A PwC survey found that 73% of B2B decision-makers consider sustainability when choosing vendors.
“Sustainability isn’t a cost—it’s a competitive differentiator in B2B.” — Rebecca Henderson, Harvard Business School
What is the difference between B2B and B2C?
B2B (business-to-business) involves companies selling to other businesses, with longer sales cycles, higher transaction values, and multiple decision-makers. B2C (business-to-consumer) targets individual customers, with shorter cycles, emotional appeals, and simpler purchasing decisions.
How do I start a B2B business?
Start by identifying a market need, validating your solution with potential clients, building a minimum viable product (MVP), and creating a sales and marketing strategy focused on value. Leverage networking, content marketing, and CRM tools to scale efficiently.
What are the biggest challenges in B2B business?
Common challenges include long sales cycles, complex decision-making processes, high customer expectations, and the need for ongoing relationship management. Overcoming these requires patience, data-driven strategies, and exceptional customer service.
Which industries are best for B2B business?
Top industries include technology (SaaS, cybersecurity), manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, professional services, and renewable energy. Any sector with complex needs and high-value transactions offers strong B2B opportunities.
How important is customer retention in B2B?
Extremely important. Acquiring a new B2B customer can cost 5–7 times more than retaining an existing one. High retention leads to recurring revenue, upsell opportunities, and strong referrals—key drivers of sustainable growth.
Mastering the B2B business landscape requires more than just a great product—it demands strategic thinking, deep customer insight, and relentless execution. From understanding core models to leveraging digital transformation and future trends, the path to success is clear. Focus on delivering measurable value, building trust, and adapting to change. The companies that thrive in the next decade won’t just sell to businesses—they’ll become indispensable partners in their success.
Further Reading: